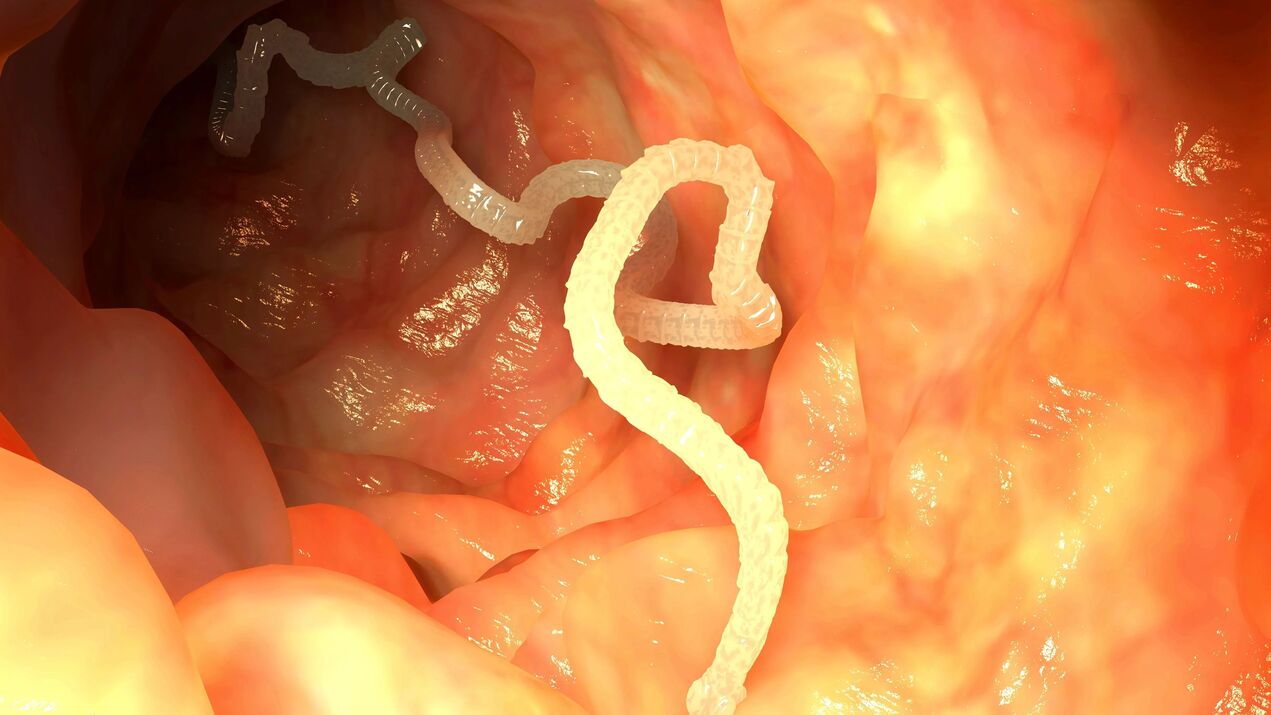
Worm infestations usually cause considerable discomfort and health problems to a person. Symptoms of worms can be very different: fever, weakness, stomach upset, headache, etc.
Worms: what are they?
As we said above, adult worms traditionally have a stable localization in the body, and their developing forms often migrate to different organs and tissues, and often the path of their movement is quite complex. For example, with ascariasis, a person becomes infected by eating foods contaminated with worm eggs (ascaris eggs ripen in the soil).
In the cavity of the intestinal tract, roundworm eggs hatch into larvae, which within a couple of hours enter through the wall of the intestinal tract into the blood vessels and are transported to the lungs through the bloodstream. Nematode larvae grow and mature in the lungs. The growing larva slowly gnaws the adjacent bronchi and crawls along them, first into the trachea and then into the oral cavity, where it is again swallowed and transported to the intestinal tract.
The roundworm larva that enters the intestinal tract develops into an adult worm. Pulmonary migration of roundworm larvae is manifested by an abundance of symptoms (cough, asthma attacks, increased body temperature, allergic skin rashes), and the presence of a small number of adult worms in the intestinal tract may not manifest itself in any way.
What are helminthiases (helminthic diseases) - Symptoms of worms

The term "helminthiasis" usually means a number of human diseases, the premise of which are various parasitic worms - helminths (another collective name for these parasites - worms).
Unlike diseases caused by bacteria, protozoa or fungi, in the case of helminthiases the number of adult helminths (worms) in the body of an infected person does not increase at a certain point (except in cases of reinfection). This is due to the fact that worms only reproduce outside the human body.
Which ones are they?
Medicine knows more than a hundred varieties of helminths. Below are the most common types of worms:
- Pinworms are small worms found in the human body that reach a length of 12 mm. This type of worm is diagnosed in the intestinal mucosa. The parasites enter the body with dust through the respiratory tract and can be easily transmitted from person to person.
- Roundworms are large roundworms that are most often found in the small intestine. Infection of the body occurs through unwashed hands and food. Most often, roundworms are found in the body of children.
- Trichinella: These parasites have round bodies no longer than 5 mm and cause trichinosis in the body. Larvae and eggs prefer to be in lightly fried meat (boar, pork, bear). In the human body, Trichinella takes up to 4 days to become an adult and its life cycle is 40 days. The main goal of this type of worm is to enter the bloodstream through the intestinal walls and settle in the muscles. Furthermore, the muscles of the respiratory and musculoskeletal systems are often affected.
- Pork/ox tapeworm. The body length of the parasite is 5-6 meters and its larvae hide in the meat of large animals (pig, cattle). The disease caused by these helminths is called taeniasis and taeniarinhoz. The larvae of both types of tapeworms are whitish vesicles attached to the walls of the small intestine. The parasite takes 3 months to reach and form an adult and the worm develops every day. The total number of segments reaches 2000, of which the final ones freely "furrow" the large intestine. Then the worms leave the body together with feces through the anus. The most common and noticeable symptom of helminthiasis is a disrupted digestive tract, as well as eating food in large quantities, and the patient does not visually gain weight.
- Necator/hookworm. The connection between these parasites is direct, due to the diseases and biological characteristics they cause. They live in the duodenum and, given their small size (10-15 mm), move freely in its environment. The larvae can only enter the body through the skin if a person has been in contact with contaminated soil. The further target of the worms are the lungs together with the digestive tract. They feed only on the blood that comes out of bitten blood vessels. As a result of the vigorous activity of these parasites, blood clotting is disrupted. Adults consume blood in the range of 0. 1-0. 35 ml per day.
- Echinococcus. In this case, a person serves as an intermediate host, because the final host is wolves, cats and dogs. Animals can become infected through direct contact with contaminated objects or people. As soon as the eggs of the parasite enter the intestine, larvae with six hooks immediately develop, which in medicine are called oncospheres.
- Whipworms are diagnosed in a person's stomach. These are thin and rather large worms.
You can determine the type of helminths by seeing what color the worms are in the feces when they emerge. Infection occurs through vegetables and meat that have undergone insufficient heat treatment. You can avoid infection by following food preparation rules.
How common and dangerous are worms?
Symptoms of worms. Data from modern epidemiological studies have revealed that every 4 people around the world are infected with worms. The incidence of worm infection is significantly higher in children than in adults. In children and adults, worms can become a prerequisite for various acquired diseases of internal organs (gastritis, pancreatitis, enterocolitis, cholecystitis) and occasionally lead to the development of dangerous complications and death.
According to the World Health Organization and the Global Disease Bank, helminth diseases rank 4th in terms of economic damage among all other diseases and injuries.
In our region there are more than 15 types of worms, of which the most common are enterobiasis (about 90% in the group of patients with helminthic diseases), ascariasis (70%), opisthorchiasis, diphyllobothriasis , trichocephalosis (60%), toxocariasis (60%) and hymenolepiasis. As follows from statistics, almost all sick people (especially children) are infected simultaneously with several forms of worms.
Where do worms spread in humans?
Many people believe that worms definitely live in the intestines, and for some types of helminths this is true. In general, worms can be found in a variety of organs and systems of the human body:
- all kinds of tapeworms, whipworms and roundworms "settle" in the large intestine;
- flukes attack the liver and gallbladder;
- Pork tapeworm larvae can spread through the bloodstream to all organs: subcutaneous adipose tissue, the eye chamber and blood vessels in the muscles can be affected.
How can you get infected with worms?
How do worms enter the human body? There are 4 main sources of helminth eggs entering the body:
Geohelminthiasis- through the soil (and then water) in which mature eggs of many helminths are found that enter the soil with human or animal feces, as well as through direct contact with animals and through the transfer of eggs by flies to food Contact - from person to man The most well-known and common worms such as pinworms are transmitted, which represent the highest risk of infection.
Biohelmintosis- when eating raw, semi-raw or slightly heat-treated meat (pork, beef) or fish infected with helminths (sushi, kebab, dried fish, lard with meat streaks, etc. ) Some parasites enter the body through insect bites
The main mechanism of any infection is most often oral-fecal, that is, a person simply swallows worm eggs along with food, water, and less often, some helminth infestations occur due to bites of infected insects. Undercooked meat and raw fish are understandable, but how can you become infected with worms through contact, household contact and soil?
Through the ground
After every contact with earth or sand, it is not enough to wash your hands, but carefully clean your nails; It is better to have short nails, especially for children. Food products growing in the soil: vegetables, herbs, fruits, berries, mushrooms, everything connected with the soil requires thorough washing under running water and scalding with boiling water. Pets, especially dogs and cats, who walk on the street bring a lot of sewage into the house and children who play with them are at maximum risk of infection; the animal can easily infect it with any type of helminths. Flies are also the main carriers of helminths, being in public toilets, places where agricultural livestock live, flies then calmly land on food, scattering eggs on their wings and legs.
From person to person
With pinworms, infection of others occurs very easily. When a female pinworm crawls out of the intestine at night, she lays about 5, 000 eggs near the anus, causing severe itching; the child, scratching the itchy area, infests his hands, nails, panties and bedding. Without washing your hands immediately, hundreds of eggs remain on all the objects you touch: door handles, clothes, food, toys. Moreover, the infection process is clear: the eggs also land on the hands of another child or adult who uses these objects and, without washing their hands before eating, end up in the mouth of a healthy person.
Through the water
A huge number of worm eggs end up in open water bodies and well water. Therefore, those who live in rural areas or in the countryside should use a bactericidal filter and be sure to boil water; It is also dangerous to ingest water when swimming in open water.
Everyone knows that worms are a problem especially for children. Firstly, because they are more susceptible to the development of helminthiasis, since the protective barriers in the children's body are not properly formed, and the acidity of the stomach is lower than that of an adult. Secondly, preschoolers, mastering the world, try all the surrounding objects not only with their hands, but also with taste. And parents, with all their desire, can teach their child to strictly follow the rules of personal hygiene, without reminders, only at the age of 3-6 years, which exposes not only the child himself, but also all members of the infection family (pinworms).
It should be remembered that no worm can reproduce and multiply in the human body, each species has its own period of time after which it dies, for example, for pinworms it is only a few weeks, for roundworms it is about a year. Eggs laid by adults must leave the body with feces or (in the case of pinworms) on the skin near the anus, in the external environment, in the soil and only then, having matured outside the human body, enter it again. , they start to become active and parasitize.
Symptoms of worms

The development of helminthiasis usually occurs in two stages: acute - from two, three weeks to two months and chronic - from several months to many years.
The acute phase coincides with the moment of introduction and development of the parasite and manifests itself mainly with an immune response to foreign antigens and allergic reactions. The symptoms of this stage of helminthiasis are similar when different types of parasites are introduced.
The chronic phase is characterized by great diversity: depending on the location of the worms, their number and lifestyle, disorders appear in the functioning of various organs and systems. Integrating into the metabolic system, consuming the necessary substances for itself, the parasite leads to disorders, manifested by disorders of digestion and absorption of vitamins, proteins, fats, carbohydrates and minerals. Worm waste products lead not only to the suppression of normal intestinal microflora, but also reduce immunity, promoting the development of chronic bacterial infections, reducing the effectiveness of preventive vaccinations.
An increased risk of malignant tumors is associated with a negative effect on the immune system and an increase in cell division (regeneration) processes in damaged tissues.
The first signs of development of helminthiasis can appear from 2-3 days (with ascariasis) to 1. 5 years (with filariasis). Most often this period is 2-3 weeks. At the beginning of the disease, skin rashes, swollen lymph nodes, enlargement of the liver and spleen, pain in the muscles and joints appear. Some helminthiases are characterized by specific signs, such as jaundice for opisthorchiasis (liver fluke) or fever, muscle pain, swelling of the face and eyelids for trichinosis.
In the chronic phase, the presence of individual specimens of worms occurs practically without any symptoms, the exception may be the presence of large specimens, for example tapeworms and roundworms. In the case of a more widespread infection, the symptoms of helminth infections consist of digestive disorders (nausea, bloating, abdominal pain, loose stools) and some specific signs. In enterobiasis, for example, it is itching in the anus, which intensifies in the evening and at night.
With whipworm it is a hemorrhagic colitis (with hemorrhages). With hookworm - iron deficiency anemia. Mechanical obstruction of the intestine and bile ducts can occur with ascariasis. With helminthiasis with liver damage, chronic hepatitis and inflammation of the biliary tract (cholecystitis, cholangitis) develop.
A special place is occupied by helminthiases with the development of cysts (liquid formations in the membrane): echinococcosis, alveococcosis, cysticercosis. Even large cysts may not manifest themselves in any way, but their suppuration or rupture leads to serious consequences such as: anaphylactic shock, peritonitis, purulent pleurisy. Helminthiasis can be accompanied by symptoms of vegetative-vascular asthenia and neurotic conditions. Let us consider in more detail the most common special cases of helminthiasis.
Worm diagnosis. Treatment of worms

With enterobiasis, the main condition for successful treatment is simultaneous deworming of all members of the family (or children's team), strict hygiene measures and repeated administration of drugs 10-14 days after the first.
Folk remedies for the treatment of worms
Traditional methods of treatment include medicinal plants that have anthelmintic and laxative effects. Even in ancient times, healers recommended using the juice of elecampane and celandine to expel worms. Carrots and carrot juice also have anthelmintic effects. Often in the recipes of traditional medicine you can find nuts, pomegranates, mint, and even more often garlic in the form of a nutritional component or enemas. A decoction of wormwood is used in the form of enemas or orally. Pumpkin seeds are an officially recognized remedy for worms. In folk medicine the use of medicinal plants is often combined with saline laxatives. Although the effect of medicinal plants is not so high, they can well serve as a prophylaxis or as an addition to the traditional treatment of helminthiasis.
Complications of helminthiasis
Complications of helminthiasis are associated mainly with the mechanical effect of the parasite on the organ; tissue destruction sometimes leads to fatal dysfunction of the affected organ. The addition of bacterial infections in places with mechanical damage is a common complication that masks the presence of the parasite in the body. For impressionable people, the sight of a parasite (for example, when it is expelled) can cause serious psychological trauma, requiring long-term rehabilitation treatment.
Prevention of worms
It contains timely identification and treatment of sick people and animals, compliance with personal hygiene measures (washing hands before eating, thoroughly washing food products, scrupulous heat treatment of food, especially meat and fish).
FAQ
What symptoms can indicate the presence of worms in a person?
Symptoms of worms may include constant fatigue, loss of appetite, weight loss, abdominal pain, itching in the anal area, and digestive problems such as diarrhea or constipation.
How can you determine if a person has worms?
To determine the presence of worms in a person, you can do a stool test for worm eggs or do a blood test for the presence of antibodies against worms. Your doctor may also order an ultrasound or other diagnostic procedures to confirm the diagnosis.
What precautions can be taken to prevent worm infections?
To prevent worm infection, it is recommended to wash your hands regularly with soap and water, especially before eating and after using the bathroom. You should also avoid contact with contaminated soil or water, drink only clean drinking water, and cook food properly to destroy any worm eggs.
Useful tips
Tip number 1
Pay attention to changes in appetite and weight. If you or your child experiences constant hunger or, conversely, loss of appetite, this may be a sign of a helminth infection.
Tip no. 2
Pay attention to the condition of your skin and hair. If you or your child develops rashes, itching, or changes in hair texture (such as brittleness or hair loss), it may be due to the presence of worms.
Tip no. 3
Pay attention to the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. If you or your child often experiences abdominal pain, constipation, or diarrhea, it may be due to a worm infection.